Traditionally, an escrow is a contract between two parties to facilitate financial transactions. An impartial third party receives and holds funds, and only releases them to the intended recipient when conditions specified by the contract are met. This method ensures both parties meet their obligations.
The XRP Ledger takes escrow a step further, replacing the third party with an automated system built into the ledger. An escrow locks up XRP or fungible tokens, which can't be used or destroyed until conditions are met.
Requires the TokenEscrow amendment. Loading...
The TokenEscrow amendment extends escrow functionality to fungible tokens, which means Trust Line Tokens and Multi-Purpose Tokens (MPTs) can be held in escrow.
For Trust Line Tokens to be held in escrow, the issuing account must have the Allow Trust Line Locking flag enabled, which allows tokens issued by the account to be held in escrow. For MPTs, the issuer needs to enable the Can Escrow and Can Transfer flags when creating the token issuance, so that the tokens can be held in escrow and transferred.
While issuers can't create escrows with their own issued tokens, they can serve as recipients. When an issuer receives escrowed tokens, the process works the same way as a direct payment.
If a token requires authorization, the sender must be pre-authorized by the issuer before creating an escrow and must also be authorized to receive the tokens back when an expired escrow is canceled, regardless of who submits the cancellation transaction. The recipient must be pre-authorized before the escrow can be finished.
The XRP Ledger supports three types of escrow:
- Time-based Escrow: Funds only become available after a certain amount of time passes.
- Conditional Escrow: This escrow is created with a corresponding condition and fulfillment. The condition serves as a lock on the funds and won't release until the correct fulfillment key is provided.
- Combination Escrow: This escrow combines the features of time-based and conditional escrow. The escrow is completely inaccessible until the specified time passes, after which the funds can be released by providing the correct fulfillment.
The lifecycle of an escrow is as follows:
The sender creates an escrow using the
EscrowCreatetransaction. This transaction defines:- An amount of XRP or fungible tokens to lock up.
- The conditions to release the funds.
- For XRP escrows this can include a time when the escrow can complete, a cryptographic condition that must be fulfilled, and optionally a time when the escrow expires.
- For token escrows similar conditions apply, but an expiration time is mandatory.
- The recipient of the funds. Any applicable transfer rates or fees are captured at creation time and will apply when the escrow completes, ensuring predictability for the recipient.
When the transaction is processed successfully, the XRP Ledger creates an
Escrowobject that holds the escrowed funds.The recipient sends an
EscrowFinishtransaction to deliver the funds. If the conditions are met, this destroys theEscrowobject and delivers the funds to the recipient. Additionally, any missing trust lines or MPT entries may be auto-created for recipients if authorization isn't required.NoteIf the escrow has an expiration time and isn't successfully finished before then, the escrow becomes expired. An expired escrow remains in the ledger until an
EscrowCanceltransaction cancels it, returning the escrowed funds to the sender.
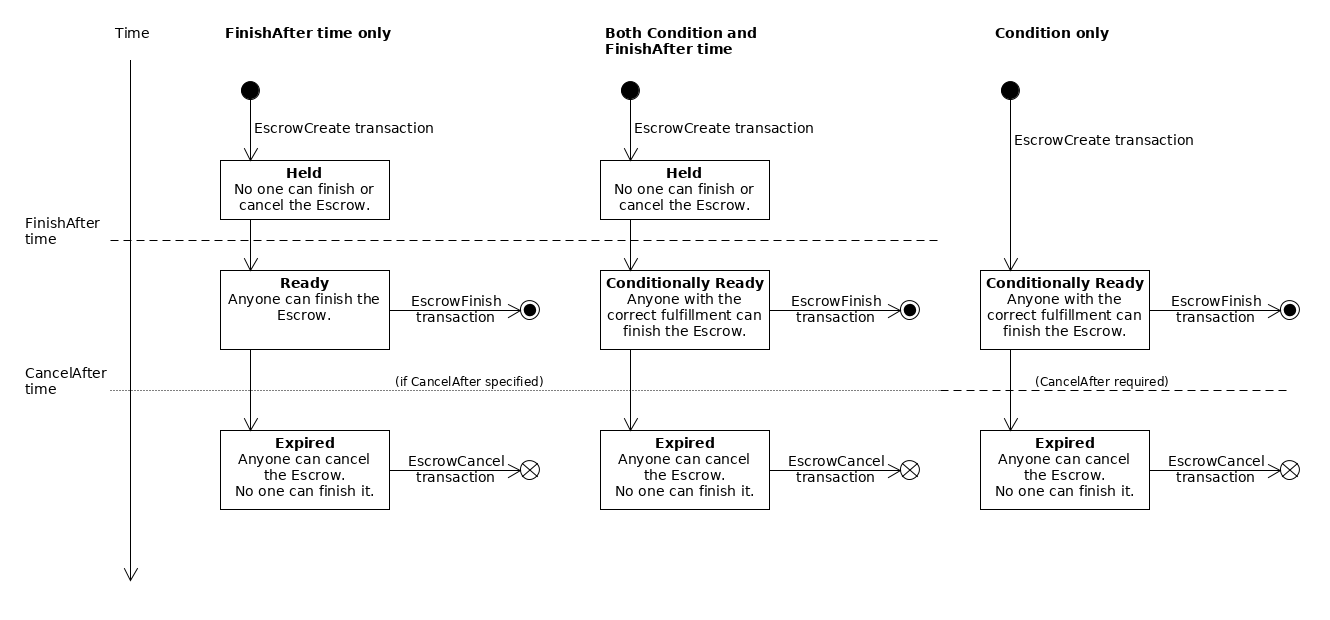
The following diagram shows the states an Escrow can progress through:
The diagram shows three different cases for three possible combinations of the escrow's "finish-after" time (FinishAfter field), crypto-condition (Condition field), and expiration time (CancelAfter field):
While XRP escrows can sometimes exist without an expiration time, token escrows must always have an expiration time (CancelAfter field).
Time-based Escrow (left): With only a finish-after time, the escrow is created in the Held state. After the specified time has passed, it becomes Ready and anyone can finish it. If the escrow has an expiration time and no one finishes it before that time passes, then the escrow becomes Expired. In the expired state, an escrow cannot be finished, and anyone can cancel it. If the escrow does not have a
CancelAfterfield, it never expires and cannot be canceled.Combination Escrow (center): If the escrow specifies both a crypto-condition (
Conditionfield) and a "finish-after" time (FinishAfterfield), the escrow is Held until its finish-after time has passed. Then it becomes Conditionally Ready, and can finish it if they supply the correct fulfillment to the crypto-condition. If the escrow has an expiration time (CancelAfterfield), and no one finishes it before that time passes, then the escrow becomes Expired. In the expired state, an escrow cannot be finished, and anyone can cancel it. If the escrow does not have aCancelAfterfield, it never expires and cannot be canceled.Conditional Escrow (right): If the escrow specifies a crypto-condition (
Conditionfield) and not a finish-after time, the escrow becomes Conditionally Ready immediately when it is created. During this time, anyone can finish the escrow, but only if they supply the correct fulfillment to the crypto-condition. If no one finishes the escrow before its expiration time (CancelAfterfield), the escrow becomes Expired. (An escrow without a finish-after time must have an expiration time.) In the expired state, the escrow can no longer be finished, and anyone can cancel it.
The costs can make it infeasible for small amounts.
- Escrow requires two transactions: one to create the escrow, and one to finish or cancel it. Crypto-Conditions incur a higher transaction cost than usual.
- While the escrow is incomplete, the sender is responsible for the reserve requirement of the
Escrowobject.
You can't create an escrow with past time values.
Timed releases and expirations resolve according to ledger close times. In practice, actual release and expiration times can vary by about five seconds as ledgers close.
The only supported crypto-condition type is PREIMAGE-SHA-256.
If a token holder is deep frozen (Trust Line Tokens) or locked (MPTs), they cannot finish an escrow to receive tokens, but they can still cancel an escrow to return tokens to the sender. Individual or global freezes for Trust Line Tokens don't prevent escrow completion.
For tokens requiring authorization, both sender and recipient must be pre-authorized by the issuer before creating or finishing the escrow, respectively. Authorization cannot be granted during the escrow completion process.
When using crypto-conditions, the EscrowFinish transaction must pay a higher transaction cost because of the higher processing load involved in verifying the crypto-condition fulfillment.
The additional transaction cost required is proportional to the size of the fulfillment. If the transaction is multi-signed, the cost of multi-signing is added to the cost of the fulfillment.
Currently, an EscrowFinish with a fulfillment requires a minimum transaction cost of 330 drops of XRP plus 10 drops per 16 bytes in the size of the fulfillment.
If Fee Voting changes the reference_fee value, the formula scales based on the new reference cost. The generalized formula for an EscrowFinish transaction with a fulfillment is as follows:
reference_fee * (signer_count + 33 + (fulfillment_bytes / 16))For more information about Escrow in the XRP Ledger, see the following: