There are several ways to run an auction, each with advantages and disadvantages.
This flow is the most straightforward. Note that the NFTokenOffer objects can always be canceled by their creator, so it's not possible to implement a binding offer.
- Store your bids in a private database.
- You take a cut of the winning bid.
- Send the buyer/seller the XRPL transaction to complete the purchase.
Run the auction in brokered mode, as an auction with a reserve.
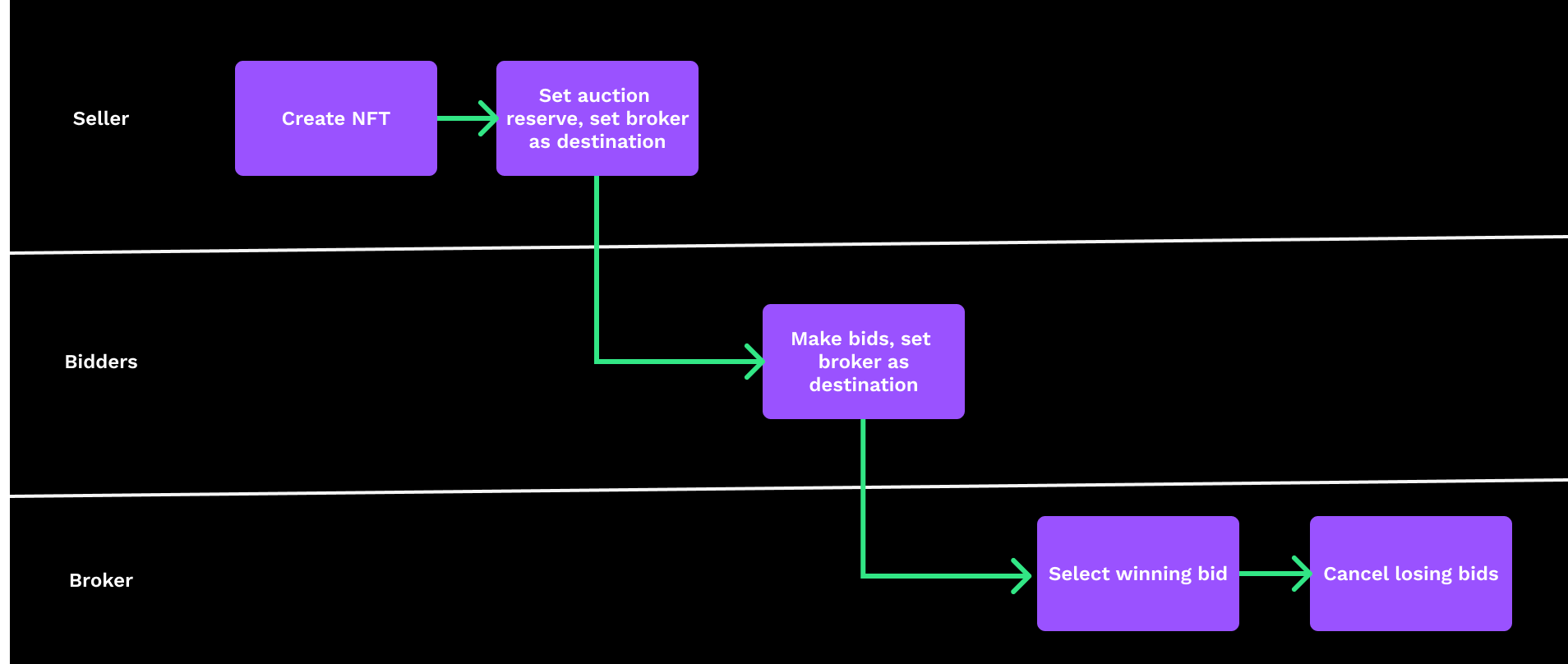
- The seller creates the NFT, then sets the auction reserve price using
NFTokenCreateOffer, specifying the broker account as the destination. - The bidders make offers using
NFTokenCreateOffer, setting the broker account as the destination. - The broker selects the winning bid, completes the sale using
NFTokenAcceptOffer, collecting the broker fee. Then the broker cancels any losing bids usingNFTokenCancelOffer.
Pros:
- The entire auction happens on the XRPL, including your broker fee.
- The seller represents their reserve price on-chain.
- This is close to a binding offer, from the buyside.
Cons:
- There must be implicit trust between the seller and the broker that the broker will not take more than some previously agreed-upon rate. If the reserve was 1 XRP and the winning bid was 1000 XRP, there is no on-chain mechanism to prevent the broker from taking 999 XRP as profit, leaving only the reserve profits for the seller.
A major mitigating factor of this downside is that if this behavior were to happen, brokers would lose their entire market share, which sellers should understand.
This is the most complex workflow of the three.
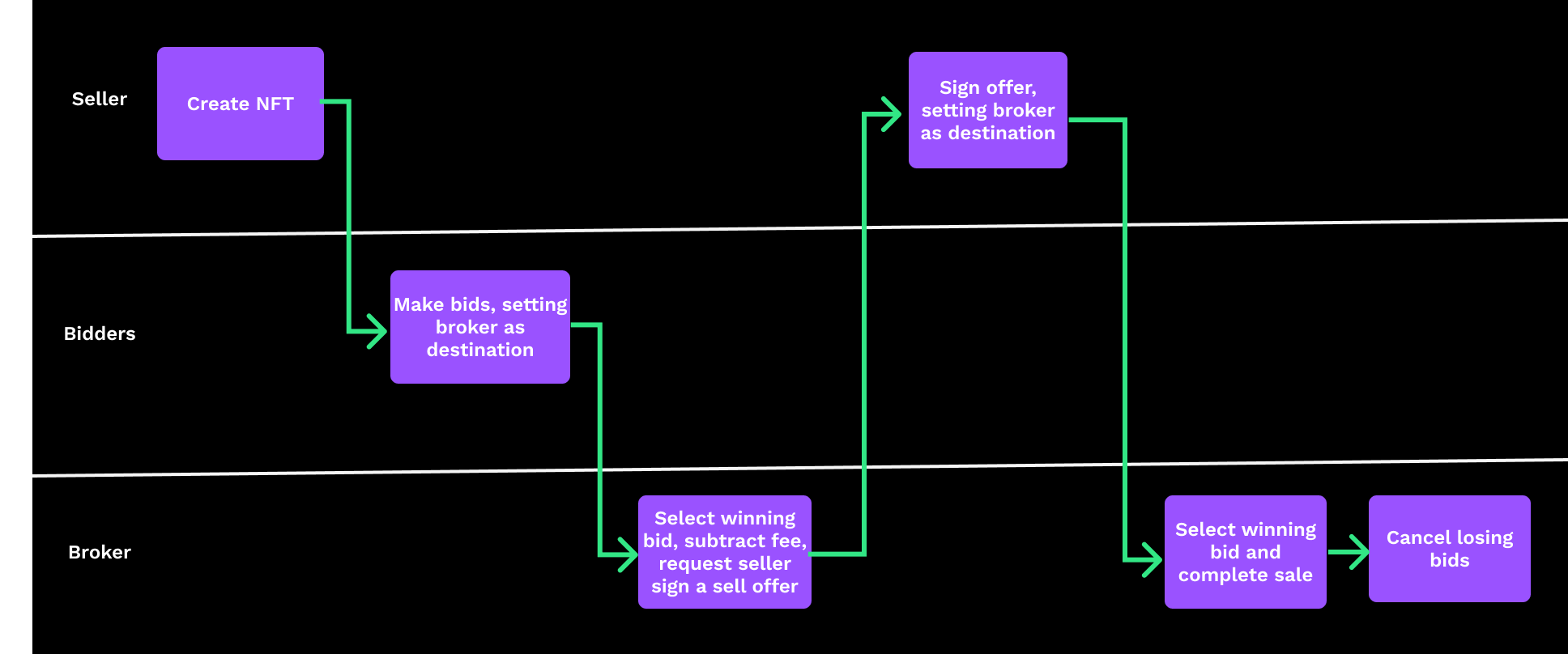
- The seller creates an NFT using
NFTokenMint. - The bidders make offers using
NFTokenCreateOffer, setting the broker as the destination. - The broker selects the winning bid, subtracts the amount to be collected as a fee, then requests the seller sign a sell offer for this amount via
NFTokenCreateOffer. - The seller signs the requested offer, setting the broker as the destination.
- The broker completes the sale using
NFTokenAcceptOffer, and receives the broker fee. - The broker cancels any remaining bids using
NFTokenCancelOffer.
Pros:
- This flow requires absolutely no trust among participants, making it the option most people expect on the blockchain.
- Sellers know exactly how much the broker takes from them in fees and must agree to it on the chain.
Cons:
- After the auction is complete, the sale is contingent on the seller agreeing to the final bid amount and broker fee amount. This means that sellers can back out of an otherwise complete auction or that sellers can delay settlement due to being distracted or not seeing some notification.
- After the auction is complete, a seller can refuse the winning bid, instead selling to someone else.